Ability to effectively communicate.
I communicate ideas and navigate the current digital environments by talking with people about what I know and see. I see the convergence of several learning styles and environments aligning with future of mobile learning. Improvements in content creation, access to data, technology, and socialization is accessible content all available today because of technology. Mobile learning education is conveniently integrated into daily life with our smartphones. Learning in this environment can use artificial intelligence, augmented reality, game-based learning, and techno-pedagogical integration (faculty) to reach learners where they are. Technology is advancing at an exponential rate bringing mobile learning into a completely immersive experience. Web 2.0 offers anytime anywhere resources that are effective with modern learning experiences. People tend to use new technology in old paradigms. Instead, new technologies have to use meaningful integration that gives students the knowledge and application appropriate for the future.
In my paper The Intergalactic Space Exploration Collaborative Training Initiative, I apply my instructional design skills to a very futuristic situation where training is needed to help crew members complete a mission. I used communication objectives to align the collaborative training for future astronauts in this paper. You can see the paper by selecting the button below.
Something I always want to communicate is the key role of designing structure to content. Breaking up content into smaller chunks makes it easier to digest and retrieve information later. I think creating concept maps communicate the knowledge level of the learner to the tutor. Concepts connected by learning models and objectives are good gauges of student understanding. They are used in learning systems to build individualized content for each person. Just like formal constructs such as language, drawing, and paintings are used to express thoughts, concept maps capture a vision of the user's perceived knowledge. They aim to aid learning systems to make good judgments about the placement of the learner into the environment. They communicate students level of understanding.
I can’t speak enough about the importance of the storyboard in the eLearning environment. Instructional Designers know that the final product is only as good as the preparation that went into creating it. Finished products shine because time and preparation are applied to a procedure. Storyboards are the foundation for the process of creating learning systems. Storyboards help to bring clarity, simplicity, ownership, and guidance. They communicate to the team how the course should be built.
Produce clear, concise, and true messages.
I Follow the code of ethics! It helps Instructional Designers navigate the variety of issues which arise during projects. Having guidelines creates a standard for measuring the implications of complicated situations. Information Technology professionals have to balance integrity and ability to guide our actions. It’s hard sometimes to remove yourself from the project. Having a solid evaluation process is the best way to protect yourself from unethical situations.
Theories of cognition do not give us the truth. But they do provide a framework for analyzing data. People generally don’t like to be defined by the limitations of their environment but in many ways they are. To produce clear, concise, and true messages in digital media I think it is important to understand how people learn.
What is the role of the brain? Is the brain limited by some kind of internal code? Like DNA. Is it predisposed instincts or is knowledge learned? What came first, learning or the instinct to learn? Either way, learning seems to be determined by one’s environment. If life is predisposed then the brain is trying to solve the universal codes hidden within its operations. Whereas naturists place cognition inside the learner because it reveals itself at the appropriate time. Watch children who spontaneously create new schemes of behavior. As if the environment unlocked the appropriate file. Most likely both nature and nurture work together. The nurturer will agree, there are encoded functions in human systems that are operating. As well, the naturalist will agree that the environment is essential to predisposed sequences. Individuals make sense of their environment through communication with their surroundings. There are many things our senses can not perceive like certain color spectrums, light waves, sound wavelengths, etc. We can measure their existence yet not experience their grandeur. In this paper below, I was having fun with creating and deciphering my own learning theory. I tried to communicate the importance of learning and why Deconstructivism is the new learning theory that gets humans one step closer to unlocking the whys of cognition. Check out my Personal Learning Theory Paper by selecting the button below.
Deliver effective and engaging presentations.
When I need to present engaging material I like get the learners attention. In the examples below I write and sketch about learning theories to inform colleagues and partners about my favorite learning applications. I start with behaviorism, cognitive information processing, schema theory, and situated cognition. Learning theories use environmental situations to initiate cognition. I have built a digital sketch of learning theories and system technologies that help me deliver a framework for presenting learning technologies to stakeholders. Check out my digital sketches by selecting the button below.
Check out some of my writings about learning theories and how they apply to Instructional Design by clicking the button below.
Produce visuals that adhere to the principles of design and use relevant applications to communicate with learners, clients, and other stakeholders.
In the E-learning market, Instructional Designers use technologies to facilitate the learning process anywhere and anytime. It is the future of learning. People act like learning stops after school however, we all know it never stops. E-learning and adaptive technologies make learning more accessible and create opportunities for lifelong growth. Below are examples of how I communicated with learners, clients, and stakeholders about building an adaptive model for E-learning environment.
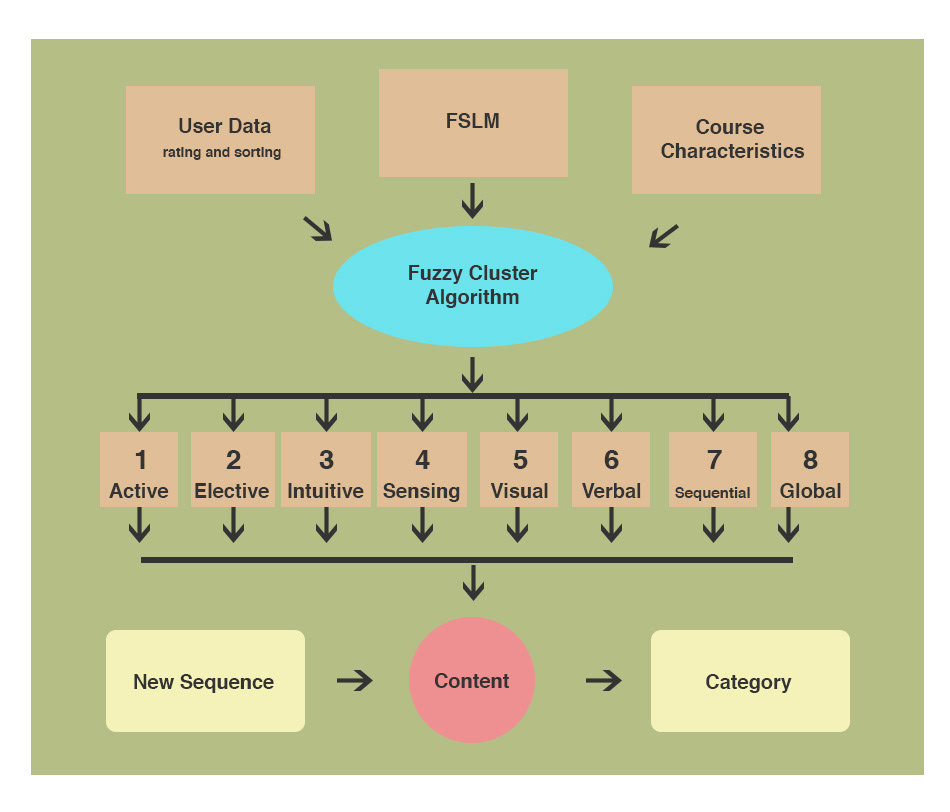
Fist a quick review of adaptive models. They are learning platforms built on the scientific method. It's a system that uses pattern recognition, statistical modeling, predictive analytics, statistical regularities, and other forms of advanced adaptive capabilities to reach learners. It’s a rule-based system with shallow adaption abilities. The learning path is determined by rules that can change for individual learners. The learner model uses an advanced algorithm to adapt the system in real-time. Feedback is generally provided once the unit is concluded. The learner is aligned to the content model which is a whole decision tree of possible materials for learning.
When trying to create an adaptive learning system I wanted to map out individual content domains and parsed it out. Content is easier to digest for users and build with adaptive systems when it is broken into smaller pieces. This allows the content to be lengthened, made more difficult, styled, converted to audio, captioned, and so on.
Here are some job aids and examples of my reasoning and documentation of the project.
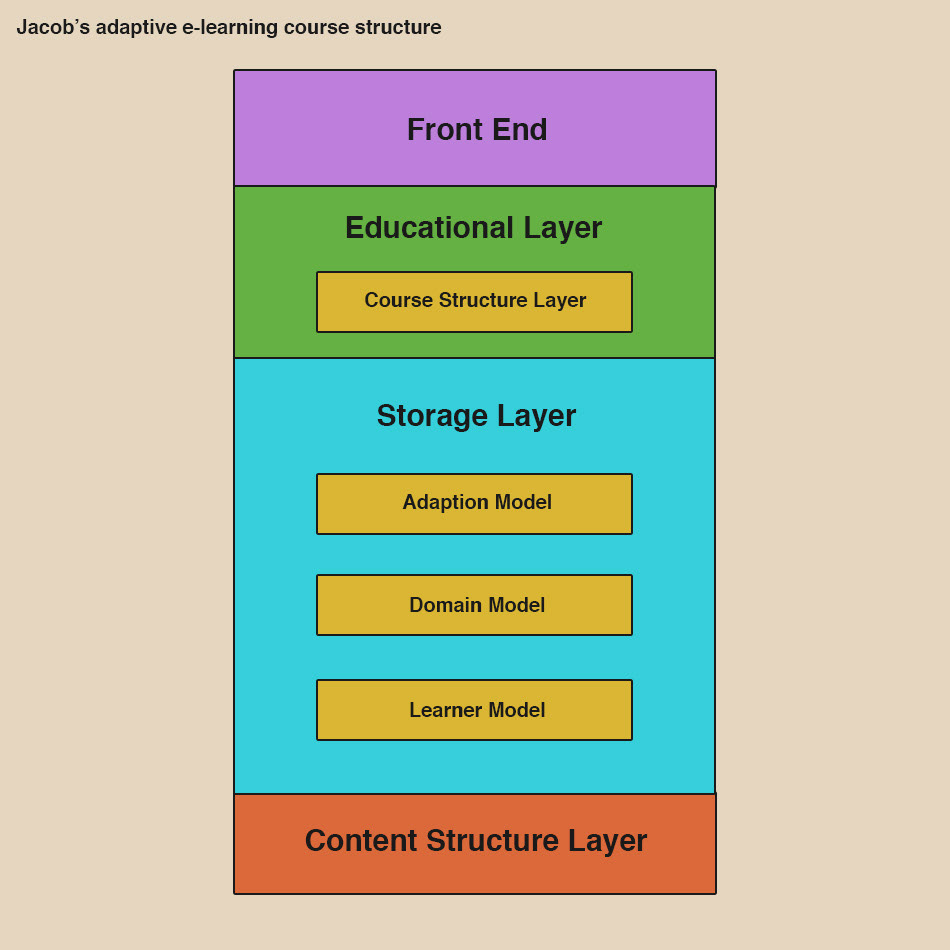
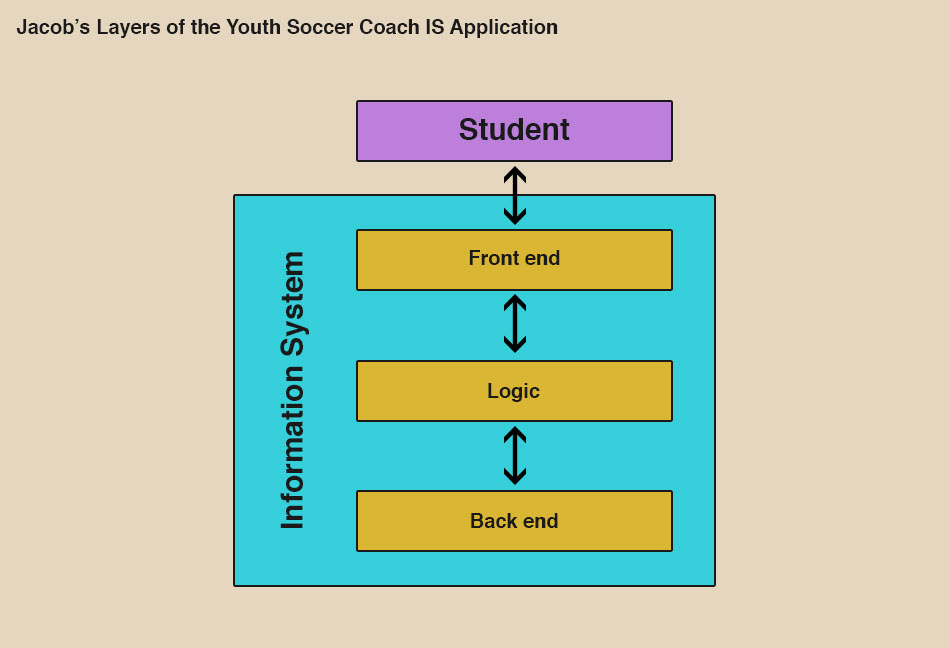
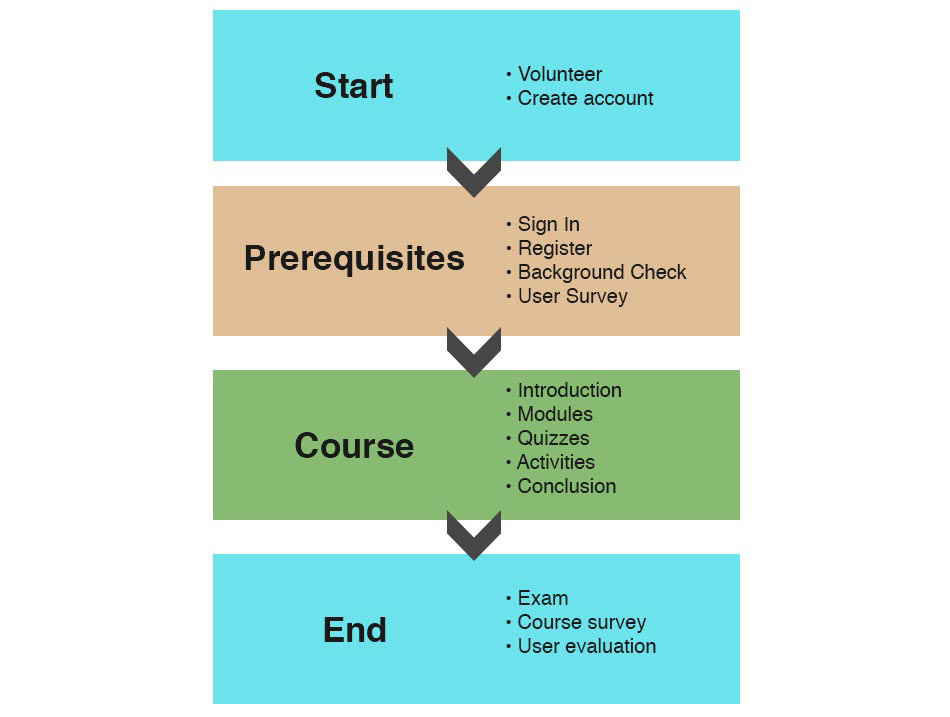


I worked on building a learning system for the Tallahassee Parks and Recreation Department to deliver an individualized one-hour learning experience/curriculum to familiarize volunteers with the responsibilities that come with coaching youth soccer. When building the structure model I used components including the domain model, course structure layer (the class diagram), content structure layer (business rules), learner model, and the front end (interface). Check out my design paper and adenium.
In my graphic, you can see how the three layers of an instructional system work within my adaptive online application. The presentation layer is the most visible piece of the adaptive system. In this layer, the system communicates with the student. Also called the graphical user interface (GUI) is where the users can interact with devices using graphical elements. Here the system defines the user roles and monitors the learner’s success. The logic layer gives structure to the course, provides the content, and provides communication to the learner. Adaptive systems are effective because they learn the how, what, when, where, and why of each individual. User data is stored and compiled in the student model. The information system is the resource management layer also known as the back end. This layer provides the functionality to the database and communication with the logic layer. This model uses learning objectives (LOs) to gauge where the student are in their learning. Check out my Youth Soccer Coach Adaptive Learning Environment Design Prototype by clicking the button below. This example used a lot of visuals and relevant applications to communicate with learners, clients, and other stakeholders the possibilities of adaptive technologies in learning environments.
Facilitate meetings to achieve agendas and goals through listening.
I use listening and facilitate meetings to achieve agendas and goals in the workplace. I practice using the cognitive model of emotions to assess work relationships. The model proposes there are 22 emotions like joy, distress, pride, shame, administration, and reproach. I find it helps me to understand where people are coming from. Knowing if someone is open, conscientious, extraverted, agreeable, or neurotic will help when gauging their emotional state.
I also like to use agile work processes like SCRUM that create quick iterative workflow stints. This process works best with meetings and clear communication of efforts. Each player in the development cycle has to give and receive feedback daily. The process really brings people together and focuses on productive interaction in work environments.
Promote effective questioning techniques.
I always like to understand what kind of learning is needed for the user. I ask myself does the learner need optimally guided learning, self-directed learning, or discovery learning? Are learners prepared to take on the task at hand? Are they motivated and emotionally mature enough to work independently and look after each other’s interests? Do they have the prior knowledge needed? Do they have adequate access to needed information? I don’t waste time on low-payoff activities. I avoid vague information, I don’t attend unimportant meetings, and I always try to solve problems using the resources I have.
Here are the big questions to ask when building learning applications:
Analyze: Are they ready?
Individuals: Who is evaluating?
Environment: What going on?
Uses: What is it going to do?
Stakeholder: Any concerns?
Design: What going to happen?
Implementation: Let’s get this party started?
Facilitation: Did the plan run its course?
Evaluate: Did you achieve success?